
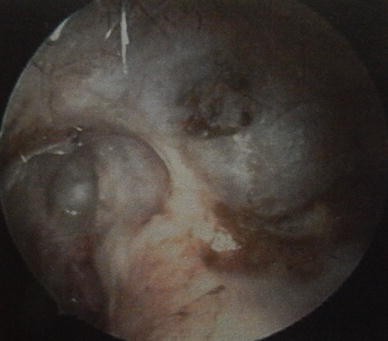
Cavity obliterated with bone dust and flap had better and early epithelialisation as compared to cartilage. Healing of cavity was better in obliterated ears. This surgery isn’t as common as it used to be. Mastoid cavity obliteration: our experience Incidence of discharge, debris, giddiness, pain was reduced in obliterated cavities. You can expect some hearing loss from a radical and modified radical mastoidectomy.
modified radical mastoidectomy, which is a less severe form of radical mastoidectomy that involves removing mastoid air cells along with some, but not all, middle ear structures. This procedure is reserved for complicated mastoid disease. radical mastoidectomy, in which your surgeon may remove your mastoid air cells, your eardrum, most of your middle ear structures, and your ear canal. simple mastoidectomy, in which your surgeon opens your mastoid bone, removes the infected air cells, and drains your middle ear. There are variations of mastoidectomy procedures, including: The procedure can also be used to remove an abnormal growth of the ear known as a cholesteatoma. The diseased cells are often the result of an ear infection that has spread into your skull. It’s filled with air cells made of bone and looks like a honey comb. The mastoid is the part of your skull located behind your ear. Cavity obliterated with bone dust and flap had better and early epithelialisation as compared to cartilage.A mastoidectomy is a surgical procedure that removes diseased mastoid air cells. Results and conclusions: Incidence of discharge, debris, giddiness, pain was reduced in obliterated cavities. The mastoid cavity is obliterated with bone pat and bone chips. Similar statements are found in the literature. Their technique consists of removal of the posterior bony canal wall with a microsagittal saw. The mastoid cavity was obliterated with either cartilage/bone dust/flaps Scientific design-prospective study. The influence of the type of surgery according to SAMEO-ATO classification on improvement of the threshold of bone conduction has not been proven in the present study, except for obliteration of the mastoid cavity (O) which is closely related to cholesteatoma presence in the mastoid cavity (M). Materials and methods: This study was conducted on 30 subjects having evidence of attico-antral type of disease in middle ear cleft. Aims and objectives: To study surgical results of mastoid obliteration, efficacy of different methods of mastoid obliteration, cavity problems and the need of cavity care. Mastoid obliteration is done to eliminate the cavity related problems. You have been recommended for mastoid obliteration surgery as your mastoid cavity is continually discharging or accumulating dead skin, and it has not improved with regular cleaning and antibiotic drops. It results in the formation of a mastoid cavity which has various problems. The general obliterative scheme utilized and extent of obliteration will vary depending on factors such as the nature of the underlying cholesteatoma, temporal bone pneumatization, and degree of. After CWDM reconstruction, a recurrence of 016.7 has been reported (Gopalakrishnan et al., 2001). The open mastoidectomy technique has been the mainstay of management of chronic ear disease however this type of surgery is not without its problem. Candidates for mastoid obliteration include both adults and children undergoing either primary or revision canal wall-down mastoidectomy surgery. The most controversial aspect of mastoid obliteration is the risk of a ‘silent’ cholesteatoma recurrence within the obliterated cavity. After mastoidectomy and certain tympanoplasty procedure, the mastoid. Having had the op explained to me I was wondering if anyone. The effect of the mastoid obliteration using palva flap and cortical bone dust. I had a radical mastoid op when I was 11 am now 45 and having serious pain so after many oils ointments and sprays this seems like the last ditched attempt. I am on the waiting list for one of these operations. The mainstay of treatment for cholesteatoma is surgery and the surgical treatment of choice is modified radical mastoidectomy. Posted 7 years ago, 7 users are following. If cholesteatoma matrix cannot be completely removed for any reason, this technique is contraindicated. Introduction: A chronic discharging ear has been a challenge for the otologists for centuries. If it is not possible to remove all cholesteatoma from the mastoid air cell tracts obliteration of the mastoid with bone pate is contraindicated.





 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
